Lower Extremity Vein : Varicose Veins : Chronic Venous Insufficiency
To clarify three similar but different words: lower extremity vein, chronic venous insufficiency, and varicose veins, lower extremity vein is not the name of a disease, but rather a blood vessel called a vein located in the legs and responsible for returning blood to the heart.
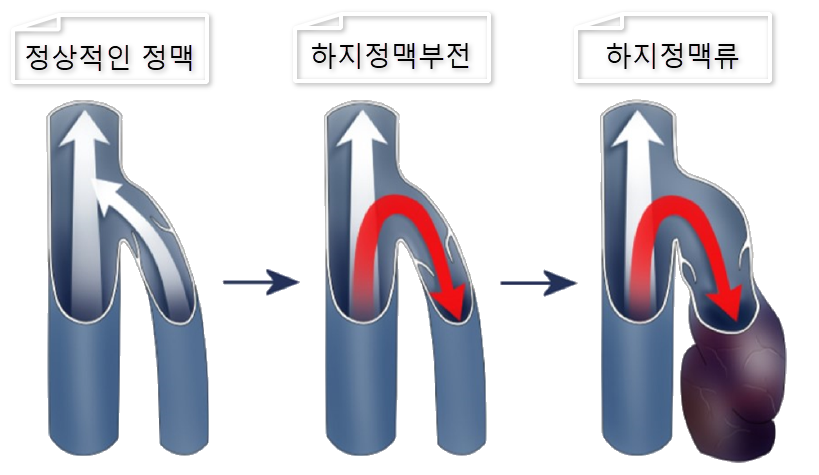
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a condition where functional impairment occurs in the leg veins, preventing blood from flowing properly toward the heart and causing it to pool in the legs. Unlike varicose veins, CVI does not involve visibly protruding veins, but it is still a condition with significant functional issues.
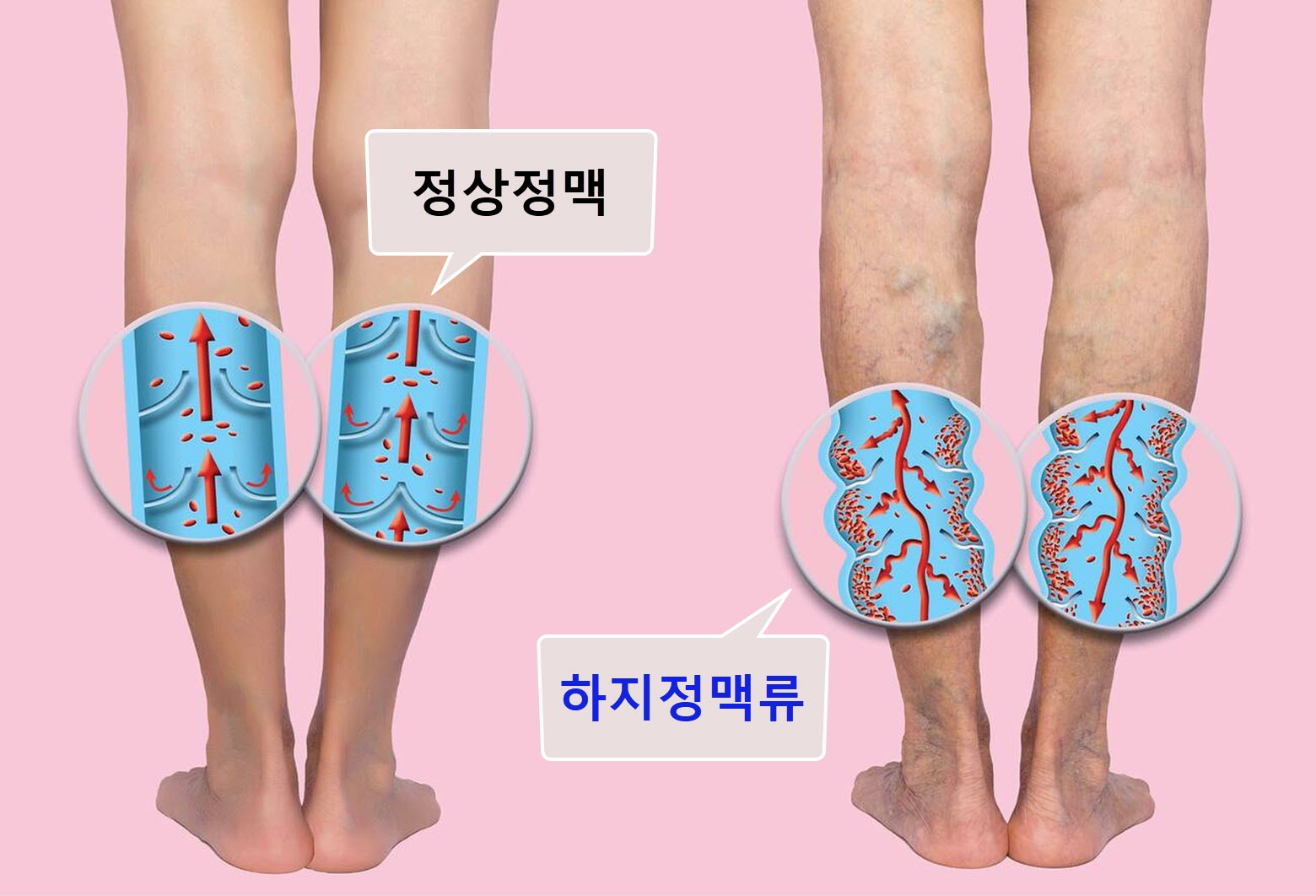
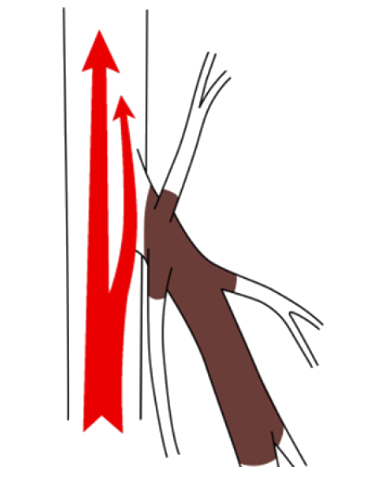
Varicose veins are apparently tortuous protrusions of blood vessels, caused by a malfunctioning valve that prevents blood from flowing normally and allows it to reverse or stagnate, causing the blood vessels to swell and protrude.
Causes of Varicose Veins
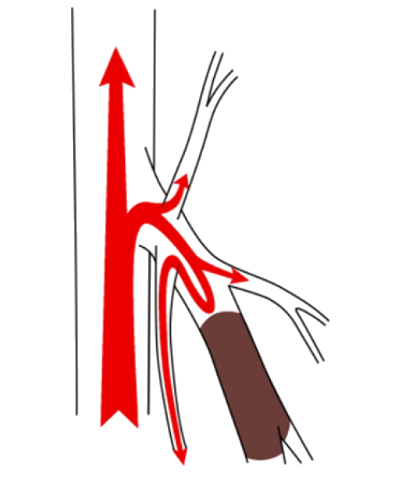
To prevent backward flow of venous blood downward, venous vessels have gates called valves. When these valves fail, venous blood that should be flowing upward instead of downward travels backwards. Instead of rising, the blood flows backwards toward the ankle and stagnates, causing the veins to stretch and develop varicose veins.
Varicose veins are caused by damaged valves in these veins, and the main causes include
- 1
Hereditary - congenital abnormalities of the vein walls and valves
- 2
Pregnancy - enlarged uterus compresses veins in the lower extremities
- 3
Aging - decreased elasticity of vein walls due to aging
- 4
smoking - increased blood viscosity and increased blood pressure lead to varicose veins
- 5
Obesity - excessive fat accumulation
- 6
Lack of exercise - standing for long periods of time
- 7
Poor diet - high in cholesterol and fat
Diagnosis and Treatment of Varicose Veins
While most varicose veins can be diagnosed with the naked eye, vascular ultrasound is essential for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
▪️ Vascular ultrasound examination
- Determine the backflow and location of blood caused by valve insufficiency.
- Identify anatomical problems with B-mode imaging and assess the direction, velocity, and volume of blood flow with Doppler.
- Diagnostic Criteria for Blood Reflux
▪ Deep veins: 1.0 seconds or longer
▪ Shallow veins: 0.5 seconds or longer
▪Perforating vein: 0.35 seconds of reflux
The varicose vein treatment you choose will be based on your condition, the size and location of the varicose veins, and your health history.
▪️ Early-stage small varicose veins: angiosclerotherapy or laser treatment is effective.
▪️ Medium-sized varicose veins: radiofrequency surgery or laser treatment is effective.
▪️ Large, complex varicose veins: may require microphlebectomy.
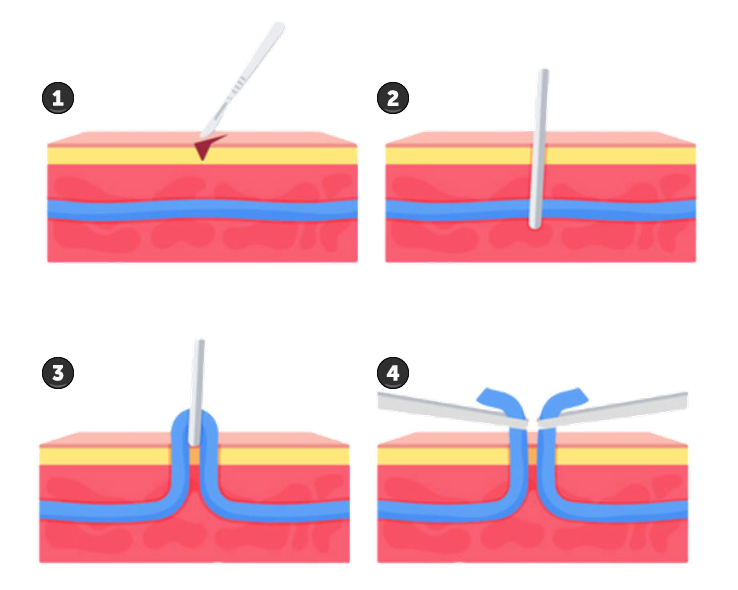
Radiofrequency therapy for varicose veins involves inserting a radiofrequency conduit into the vein and generating heat to induce vein closure. It is less painful and faster to recover from than laser surgery, and you can return to normal activities one to two days after surgery.
Angiosclerosis therapy of varicose vein involves injecting medications called sclerosants to stiffen the blood vessels and block blood flow. The process involves using vascular ultrasound to check the saphenous and penetrating veins for abnormalities, and the number of treatments will vary depending on your individual condition.
Microphlebectomy, which has been commonly performed in the past, is a treatment that directly removes the vessels with venous reflux. It is often performed at the same time as other varicose vein surgeries, but because it leaves a 2mm scar, it is often followed up for 6 months or so after surgery to see if any branching vessels remain.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
- 1
My legs are tingling and heavy.
- 2
Pain and heat sensation in the calf.
- 3
My legs itch and swell frequently.
- 4
I feel pain in the bottom of my foot.
- 5
At night, I get cramps in my legs.
- 6
My toes don't feel as good as they used to.
- 7
The skin on your leg is oozing blood and bleeding.
Complications of Varicose Veins
- 1
Skin ulcers: caused by varicose veins that prevent sufficient blood supply to skin tissue
- 2
Phlebitis: Inflammation of a vein, often resulting in pain.
- 3
Hyperpigmentation: Brown or dark spots on the skin
- 4
Chronic venous insufficiency: persistent decreased function of veins, leading to a variety of symptoms
- 5
Superficial venous thrombosis: blood clots in veins close to the surface of the skin
- 6
Bleeding: In severe cases, a vein ruptures, causing bleeding
- 7
Dermatitis: Skin becomes inflamed and itchy
Precautions after Procedure
- 1Compression stockings should be avoided.
- 2Alcohol and smoking should be avoided for up to 3 weeks.
- 3Avoid baths and steam rooms for about 1 month.
- 4Walking and ankle exercises can help you recover.
- 5
After surgery, bruising or pulling sensations may persist for 1 week to 1 month.
SH Clinic's Know-how and Before-and-After Photos
Our varicose vein treatment is a complete closure surgery that leaves the root vessels intact, eliminating the possibility of recurrence.
| Existing Closure Procedure | Complete Closure Procedure | |
|---|---|---|
| Methods | Performed leaving approximately a 5mm stump at the proximal great saphenous vein | Complete closure of the proximal great saphenous vein without leaving a stump |
|
Blood flow Stability |
The stump could not withstand the pressure, resulting in the development of a new reflux pathway | The pressure is evenly distributed to create a comfortable pathway for blood flow |
|
Recurrence Possibility |
Recurrence possible | Low likelihood of recurrence |
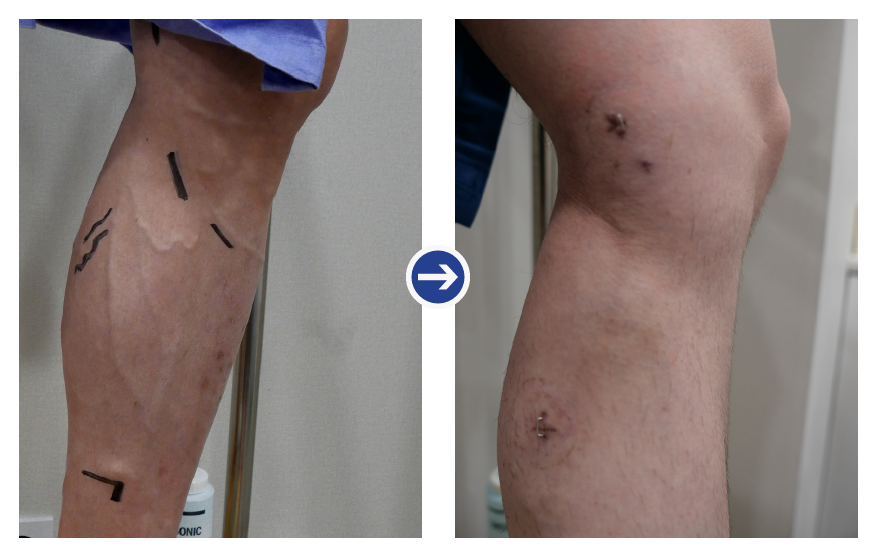
Before and after radiofrequency treatment 1
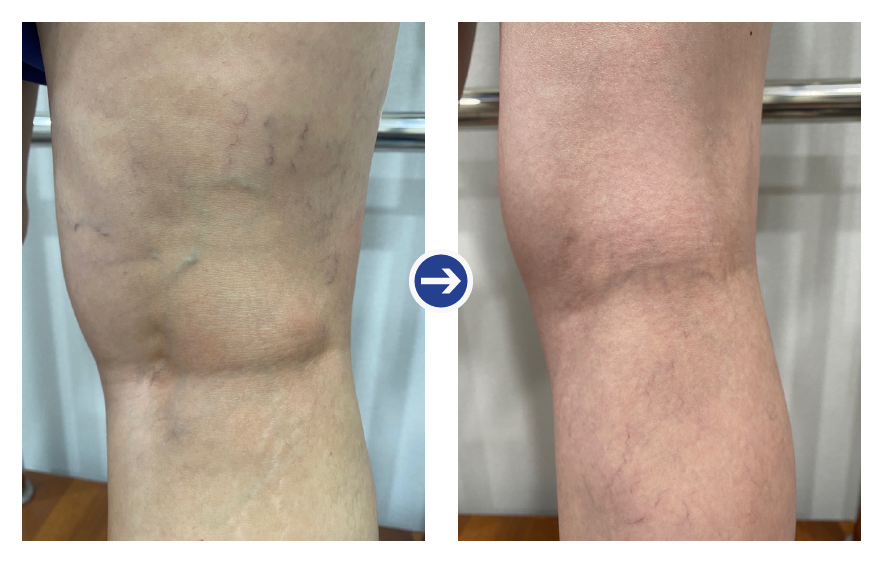
Before and after photos of radiofrequency treatment 2
Common diagnoses for people with venous pain
The diagnosis of chronic venous insufficiency is made with an ultrasound. Ultrasound can look at the blood flow in the veins, check the function of the valves or how dilated the veins are, and pinpoint if there is reflux.
- 1
Foot / leg / lower back / hip pain - spinal stenosis, herniated disc, peripheral neuropathy
- 2
Plantar Pain - Interosseous Neuroma, Plantar Fasciitis
- 3
Knee Pain - Osteoarthritis
- 4
Shoulder Pain - Frozen Shoulder, Impingement Syndrome, Rotator Cuff Tear
- 5
General Pain / Discomfort - Restless Legs Syndrome, Fibromyalgia, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Various Symptoms of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Treatments for Chronic Venous Insufficiency
The treatment of chronic venous insufficiency depends on the severity of your symptoms, and there are several options available, and it's important to work with your healthcare provider to choose the right treatment. In the early stages, non-surgical treatments are often effective, but if symptoms become severe, surgical treatment may be necessary.
Pharmacotherapy can help relieve symptoms by increasing the tone of the blood vessels, reducing the amount of reflux and inhibiting the progression of venous insufficiency. However, medication alone is not a complete cure, so it's important to work with your healthcare provider to make a decision.
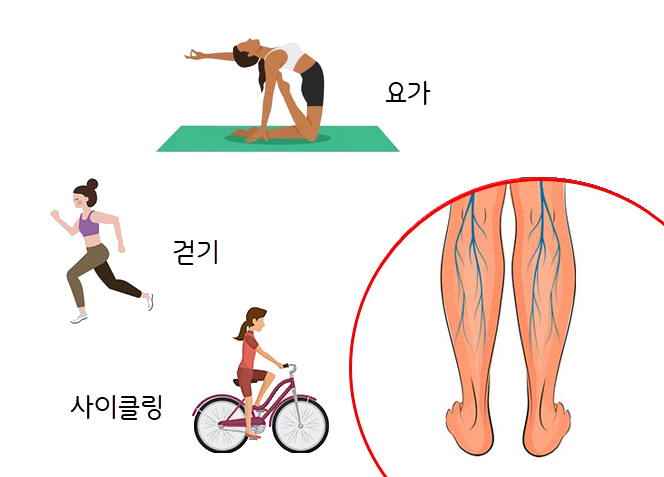
Exercise therapy is very important to improve circulation and relieve symptoms. A variety of exercises can be helpful, including walking, biking, ankle exercises, yoga, and more, and it's important to consult with your doctor before you start exercising and choose an appropriate exercise regimen.
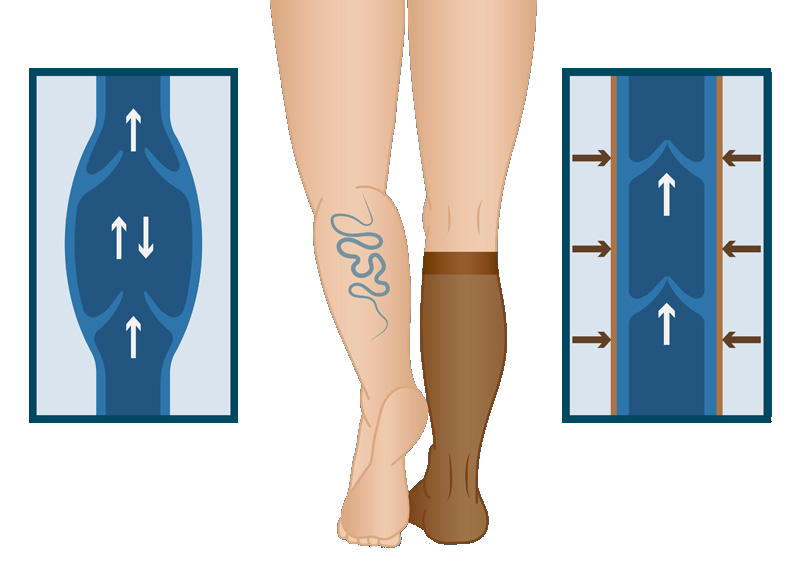
Compression stockings help to properly distribute pressure in the veins of the legs, allowing blood to flow back toward the heart and relieving symptoms.
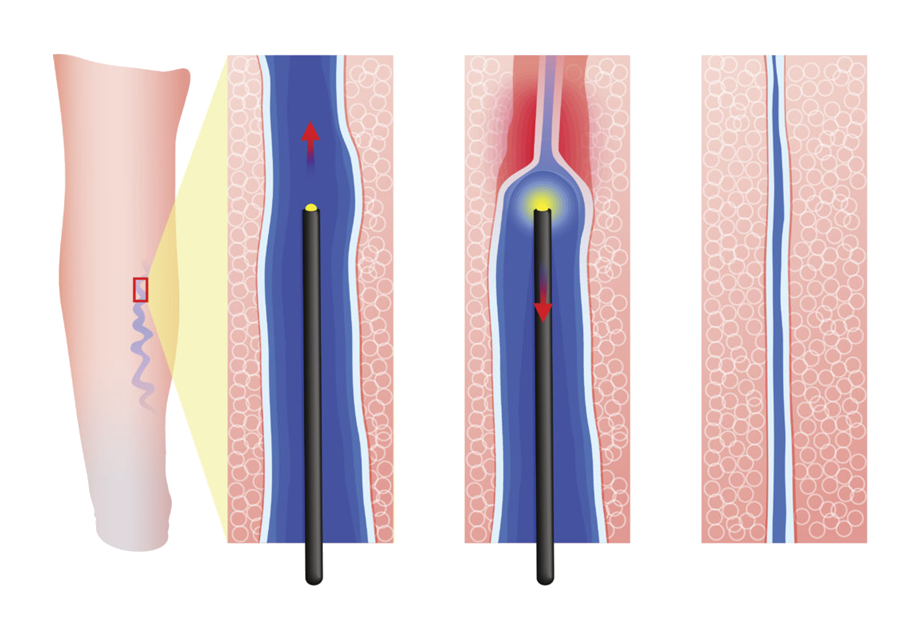
Laser therapy is a relatively new non-surgical treatment that involves closing a blood vessel with high heat, up to 1,000°C instantaneously. The closed vein no longer carries blood, and blood flows through other healthy veins. Over time, the closed vein is naturally absorbed by the body.
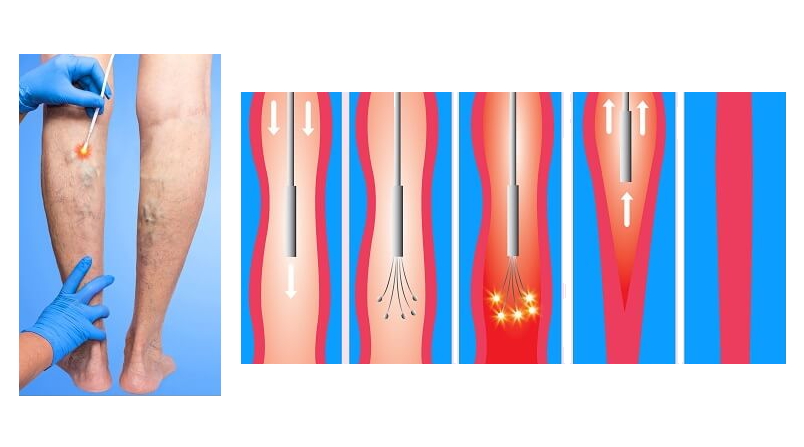
Along with laser therapy, radiofrequency therapy is one of the most popular non-invasive treatment methods in recent years, delivering relatively low heat of 120°C to the walls of diseased veins, causing them to shrink and close. Over time, the closed veins are absorbed by the body and blood flow is redirected through other healthy veins.
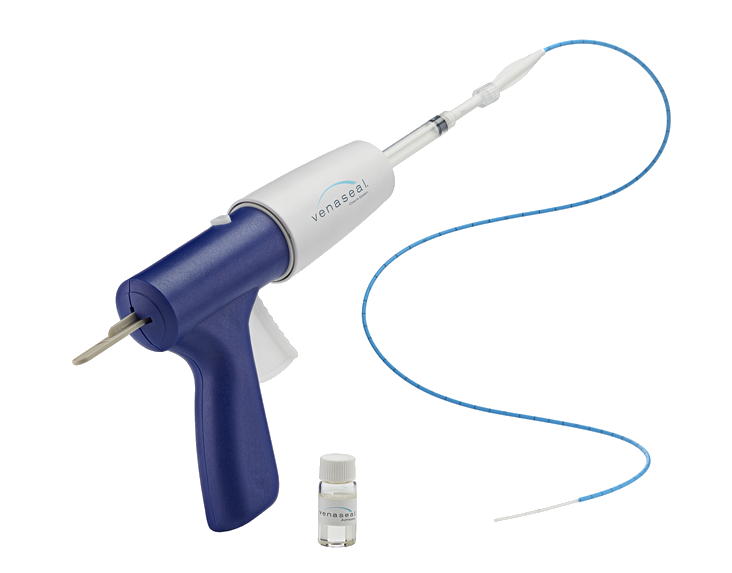
VenaSeal, a medical adhesive, is injected inside the diseased vein to close the vein, allowing it to absorb naturally over time.
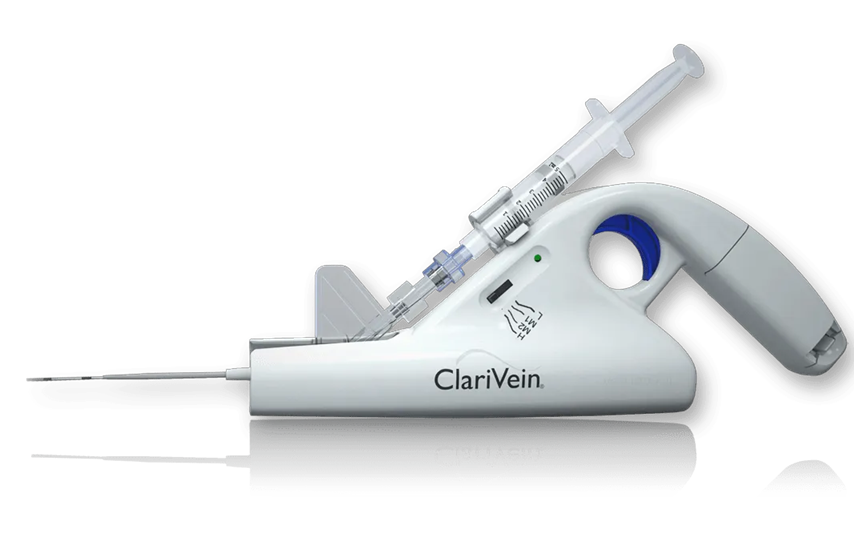
ClariVein is a procedure that combines mechanical endovascular lining damage with angiosclerotherapy to close diseased veins and restore normal blood flow. It has the advantages of fast recovery time, less pain, and no scarring.
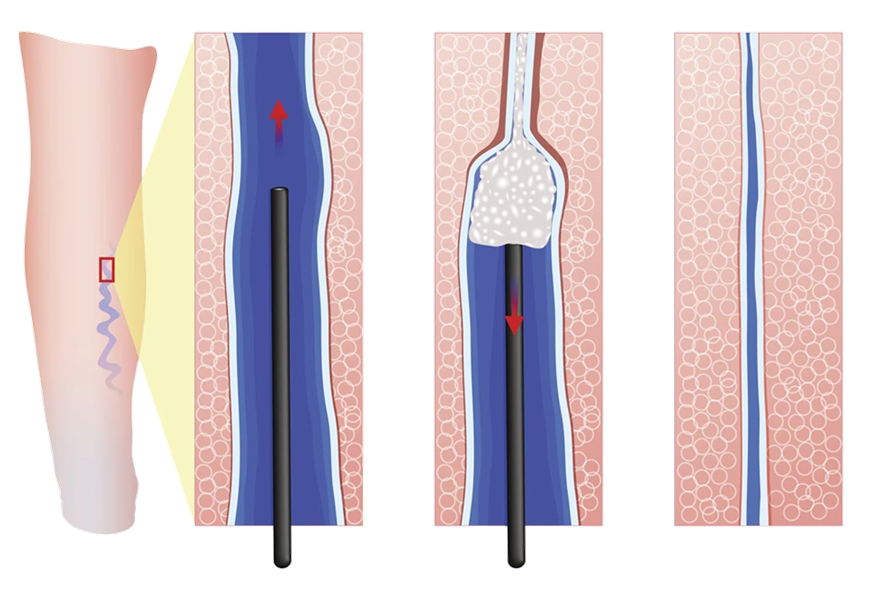
Angiosclerosis therapy involves injecting a medication into a vein, which irritates the vein walls, causing them to stick together and block blood flow. Over time, the closed vein is absorbed by the body and disappears. This treatment is particularly suitable for small varicose veins or spider veins.
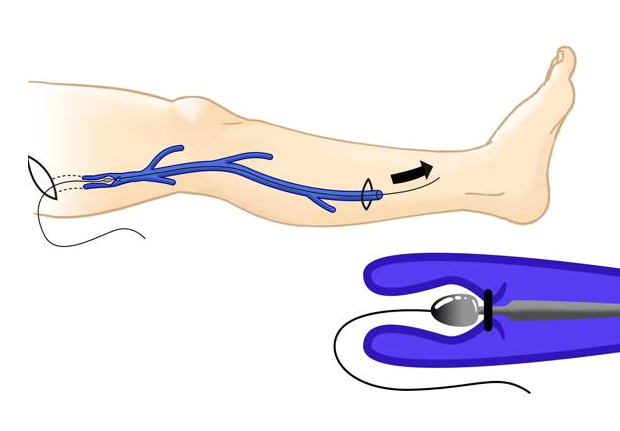
Stripping is performed on severe varicose vein patients and involves directly removing the affected veins with minimal incisions. A stripper is inserted to physically extract the enlarged or abnormal veins, restoring normal blood flow.