Radiofrequency Myolysis with Good Results
Radiofrequency myolysis is a method of treating fibroids by inserting a needle that generates radiofrequency waves into the center of the fibroid or adenomyosis and using the high-frequency heat (about 250°C) from the tip of the needle to treat the fibroids.
It is a widely used treatment because it uses radiofrequency and is minimally invasive and effective.
- 1
Semi-sedated anesthesia allows for a shorter procedure time and no after-effects, allowing for same-day hospitalization and discharge
- 2
Treatments that minimize damage to the uterus allow for normal pregnancy
- 3
No scarring from surgery and little long-term adhesions after the procedure
- 4
There is little bleeding during the procedure and symptoms improve quickly
- 5
The procedure is available for any number and size of fibroids
- 6
If you relapse, it's easy to get back on track
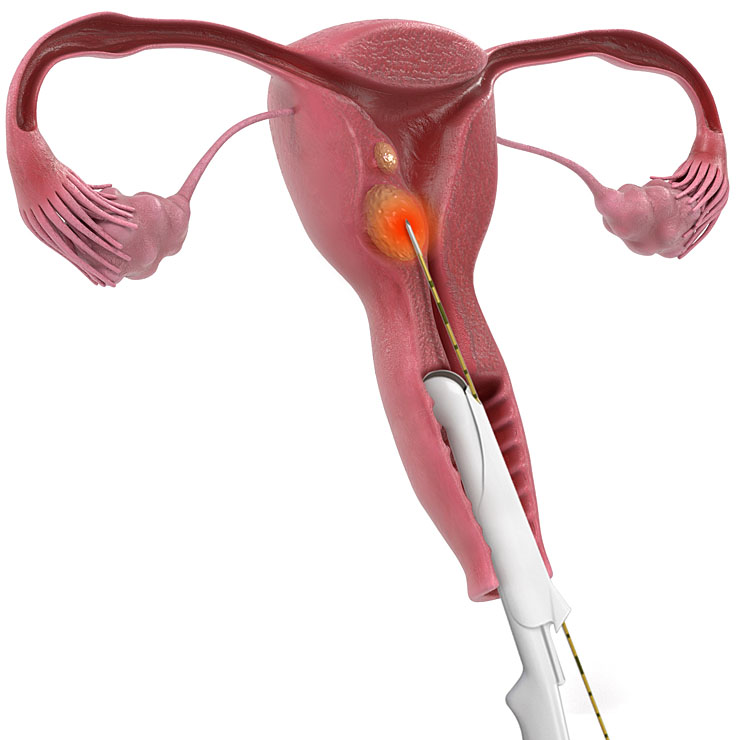
How does radiofrequency myolysis work?
The most recently developed radiofrequency myolysis utilizes high-frequency heat delivered through a thin electrode to necrotize uterine fibroids. During the procedure, the patient's condition is continuously monitored, allowing for immediate intervention if necessary.
This surgery provides excellent pain relief and bleeding prevention, and because it prioritizes uterine preservation, it is an appropriate treatment for young women considering future pregnancies.
Side Effects and Precautions of Radiofrequency Myolysis
Although radiofrequency myolysis is generally a safe procedure, some side effects can occur. The main side effects and precautions include
- 1
In rare cases, there may be a risk of skin burns.
- 2
You may experience some vaginal discharge after the procedure.
- 3
It is recommended that you refrain from smoking, alcohol, and strenuous activity after your procedure
- 4
Rarely, side effects such as bleeding or pain may occur after the procedure, and if they persist, you will need to come in for an appointment.
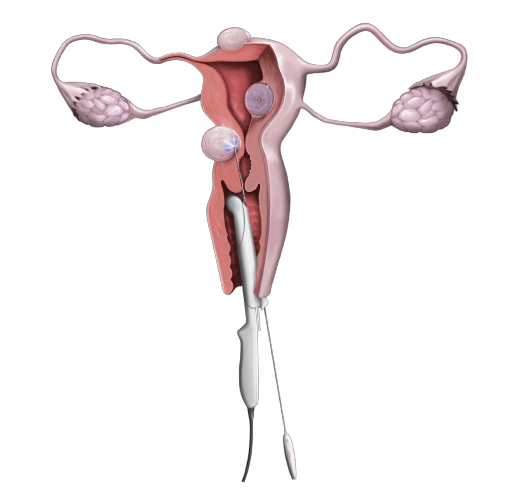
Why you need uterine myoma treatment before pregnancy
The endometrium is the part of the uterus where the baby implants, and the presence of fibroids in the endometrium can interfere with implantation, and treatment will be determined by the size and growth rate of the individual's fibroids.





