The most common tumor in women Uterine myoma
Uterine myomas are benign tumors that develop from the smooth muscle that makes up the majority of the uterus and are common in women in their 30s and 40s.
The exact cause is not yet known, but female hormones (estrogen) and genetic factors may play a role.
Although uterine myomas are not cancer, they can cause a variety of symptoms depending on their size, number, and location, so it's important to detect them as early as possible through accurate screening so they can be treated appropriately.
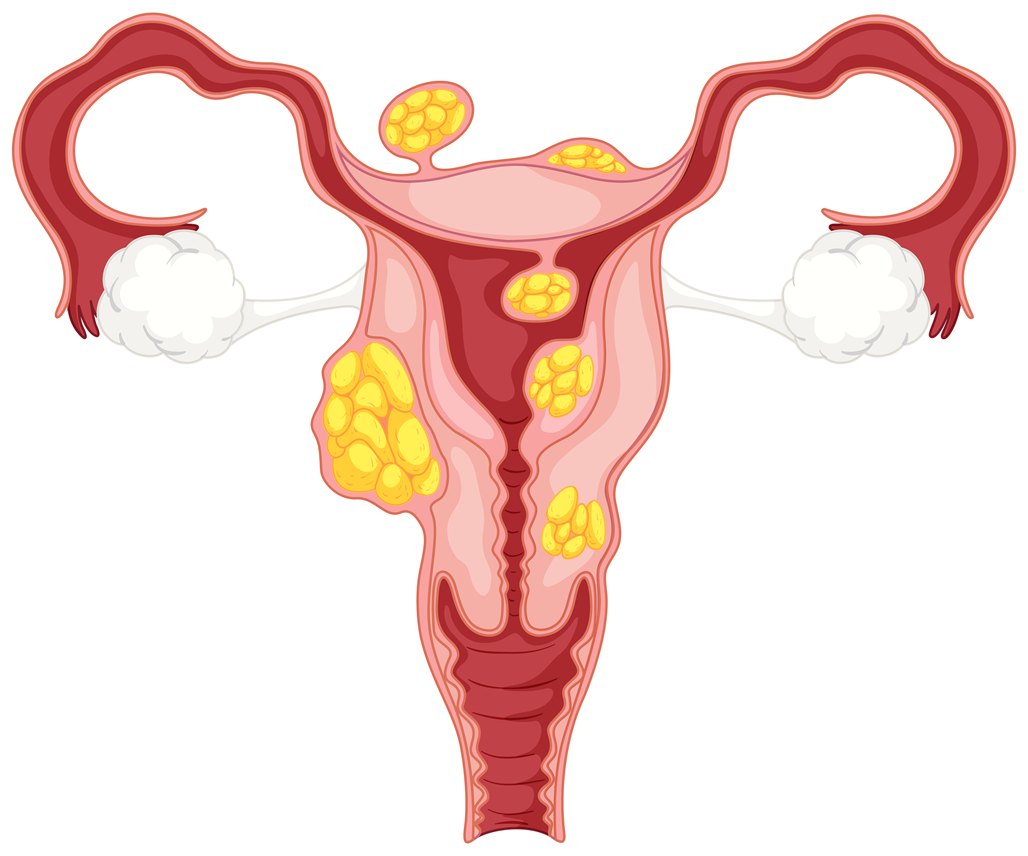
Symptoms of Uterine Myoma
About 10% to 20% of uterine myomas cause the following symptoms, depending on their size, number, and location. If they interfere with your daily life or grow larger, you should seek treatment.
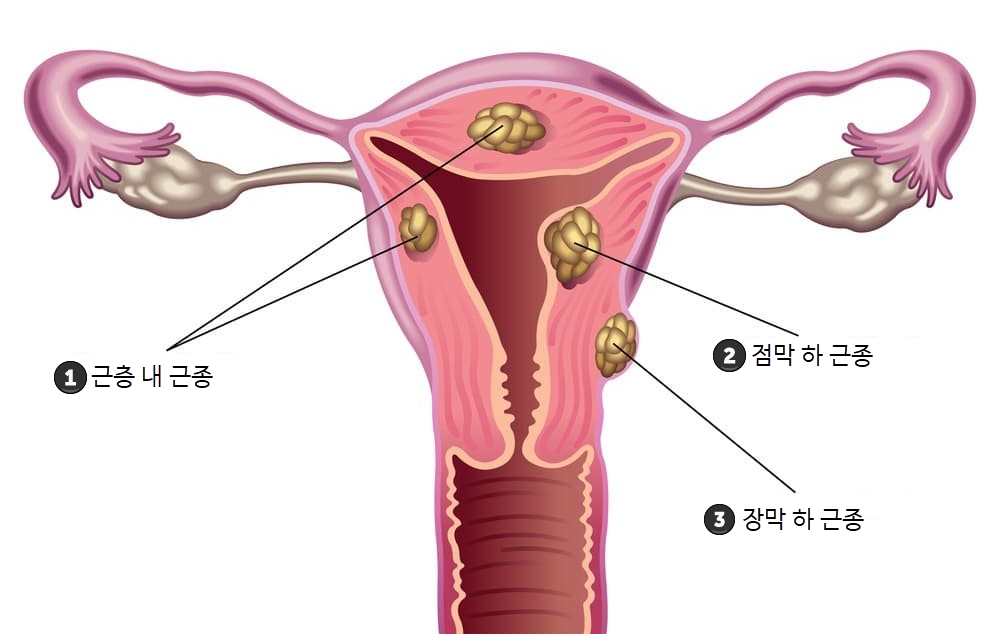
Types of Uterine Myoma
Uterine myomas are classified based on their location within the uterus: intramural, subserosal, and submucosal fibroids. Their size tends to increase due to the influence of female hormones and growth hormones.
Treatment of Uterine Myoma
The treatment of uterine myoma can vary depending on the size, location, and symptoms of the fibroids, as well as the patient's age and health.
- 1
Medications - It may temporarily help reduce the size of fibroids or relieve symptoms, but it is not a cure.
- 2
Non-surgical HIFU Procedures - An advanced treatment that uses ultrasound to destroy fibroids without incisions
- 3
Surgical treatment - There are myomectomies and hysterectomies.
Why you need uterine myoma treatment before pregnancy
The endometrium is the part of the uterus where the baby implants, and the presence of fibroids in the endometrium can interfere with implantation, and treatment will be determined by the size and growth rate of the individual's fibroids.