Adenomyosis, an increase in the size of the uterus
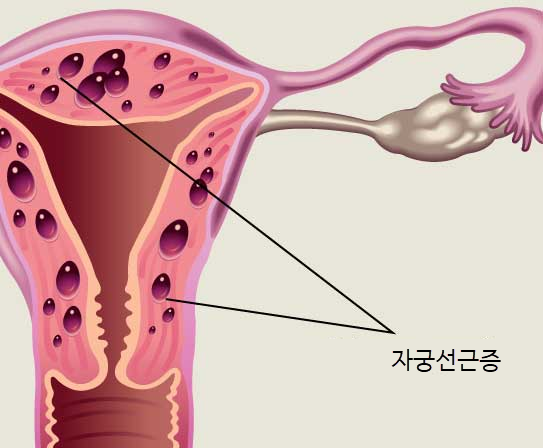
Adenomyosis is a condition in which tissue from the endometrial layer, the innermost layer of the uterus, invades the muscle layer of the uterus.
Endometrial tissue has the property of increasing in size with the menstrual cycle, and endometrial tissue that invades the muscle layer of the uterus gradually pushes out the surrounding tissue and increases in size.
Causes of Adenomyosis
Although the cause of adenomyosis is not fully understood, it is believed to be caused by genetic factors or an imbalance in hormone secretion in most cases.
Symptoms of Adenomyosis
It causes the uterine tissue to produce more blood than normal and increases the contraction of the uterine muscles, the release of inflammatory substances, and nerve overstimulation, resulting in severe, squeezing menstrual cramps that can cause infertility and, in severe cases, infertility.
Difference between Uterine Myoma and Adenomyosis
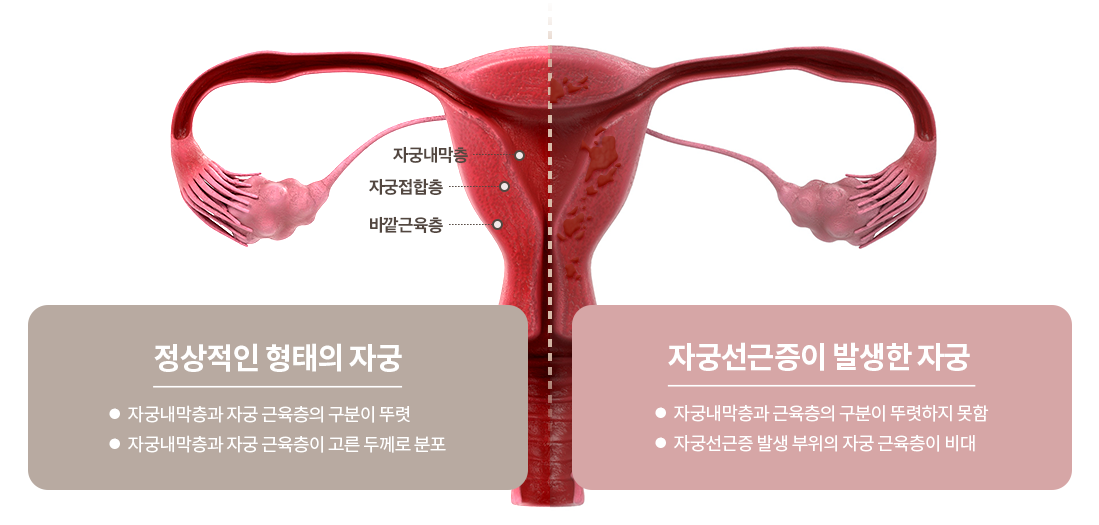
Uterine myoma and adenomyosis are similar but different conditions. Whereas uterine myomas are lumps, adenomyosis is a thickening of the uterus caused by abnormal growth of the endometrium into the uterine tissue.
In addition, unlike uterine myoma, adenomyosis is difficult to treat because the boundaries of the disease are unclear and the lesions are sporadic.
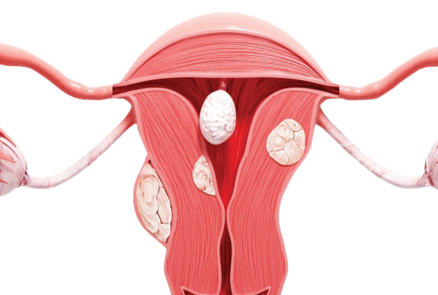
▪️ Tumors in which the muscle layers of the uterus are clumped together in a mass
▪️ The presence or absence of symptoms depends on the size and location of the fibroids
▪️ The lesion has a distinct boundary with the surrounding muscle layer, making it relatively easy to detect and remove.

▪️ Endometrial tissue abnormally proliferates in the muscle layer
▪️ if you have adenomyosis, you are more likely to have symptoms
▪️ Unclear boundaries between the lesion and normal tissue make treatment and removal more challenging
Treatments for Uterine Myoma and Adenomyosis
Most uterine myoma and adenomyosis can be treated with the HIFU procedure, but the effectiveness of the treatment may vary depending on the size, location, and type of lesion.
In some cases, surgical excision may be more appropriate, so it's important to get an accurate diagnosis of your uterine condition to determine if you're a good candidate for a haifu procedure first.
| HIFU | Myomectomy | Hysterectomy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Principles | Without anesthesia or incision, high-intensity ultrasound is used to necrotize only the fibroids, resulting in no pain or bleeding. | Three small incisions are made in the navel and lower abdomen, and surgical instruments are inserted to remove only the fibroids. | A surgery in which an incision of about 7cm is made in the lower abdomen to remove the entire uterus. |
| Length of stay | Daily routine the day after your procedure | 4 to 5 days | 5 to 7 days |
| Precautions | There is a possibility of mild burns or slight blisters. | The possibility of damage to surrounding organs or adhesion | Pregnancy is not possible, and there may be mental and physical aftereffects. |